Remote references
Hackolade Studio is built on a very modular architecture which allows to compose a model from pieces of one or more models. These references to external definitions are described in this page of the documentation, and in this how-to guide.
An external reference points to an object that belongs to another data model or JSON Schema. More specifically, it makes it possible for an entity, an attribute, or a sub-attribute of a data model to reuse structure defined elsewhere - in another data model or JSON Schema, this structure being:
- an internal definition
- a sub-attribute of an internal definition
- a model definition
- a sub-attribute of a model definition
- an entity
- an attribute
- a sub-attribute
- an object from JSON Schema
Note: an external reference does not necessarily point to a definition. All existing entities and attributes of the referenced model can be used as "definitions" -- without any special preparation for the fact that they can be reused elsewhere.
This modular architecture is also applied to Polyglot models, and specifically to the fact that you can compose a derived model from pieces of one or more Polyglot models, as described here.
In both cases, external references, and Polyglot references, you currently open model must be linked to another model file. It is possible for references to be based on a file path of your local file system, preferably to a locally-clone repository. Note that relative paths are almost always better than absolute paths.
Previously , there were a couple of limitations with external references being to a file path. First, it meant that both the referencing model and the referenced models were both in the same repository. While doing cross-repository references was technically possible, it was a fragile reference that depended on all users cloning the different repositories locally in the exact same manner. The second issue was related to the browser-based deployment of Hackolade Studio, because browsers have security-related restrictions regarding local file systems.
With v8.7.0, Hackolade Studio includes support for remote references. A remote reference is an external reference or a Polyglot reference that can be in a remote location, typically a remote repository. Specifically, this capability allows to reference a model in the same repository (whether cloned locally, or access directly), in a different repository of the same repo provider, or even in a repository of a different repo provider. A remote reference is not a distinct type of references: it is rather a runtime characteristic of a reference to another model. Remote references also allow Studio in the browser to create and update external and Polyglot references.
Monorepo vs multi-repo
Hackolade persists models and schema artifacts as JSON in Git, and expects them to follow the same lifecycle as application code branches and CI/CD pipelines. The “single source of truth” is “a Git repository (or set of repositories)” that may also contain application code, contracts, and generated DDL / schema contracts.
It is common to wonder about the best way to organize the repository and ask the question of whether this should be a single repository or more.
Monorepos suit scenarios with tightly coupled code and models, facilitating atomic changes across services, global refactors, and unified CI/CD pipelines in a single repository, though they risk performance issues fromcoarser access controls.
Multi-repo approaches align better with domain isolation, independent lifecycles for models like warehouses or MDM, and fine-grained permissions per repo, but they complicate cross-domain updates requiring multiple PRs and duplicated tooling.
Practically, co-locate Hackolade artifacts with related code for atomic evolution, use consistent branching and CLI exports in CI regardless of structure, and opt for monorepo if leveraging existing monorepos with loose team boundaries, multi-repo for regulated or siloed domains, or hybrids per platform.
No matter your choice, rest assured that the modular architecture of Hackolade Studio remains applicable
Intra-repository references
The primary use case for references is in a monorepo environment supports references:
- from a model that belongs to a Git repository
- to another model that belongs to the same Git repository.
Hackolade Studio supports 2 ways of editing a model that belongs to a Git repository:
- It is possible to open a local clone in the desktop app and to perform all kinds of Git operations: checkout (new) branch, commit, pull, push, etc. Note that this is not supported in the browser app.
- It is possible to open a model directly from a remote repository - without cloning it first - using Open From in both the desktop app and the browser app.
Of course, the solution is portable across those use cases. For example, it is possible to refresh in the browser app a reference that has been created between 2 models of a local clone using the desktop app. Or vice-versa: it should be possible to create a reference in the browser app and to refresh it from a local clone in the desktop app.
The solution is actually quite simple:
- an intra-repository reference is persisted as a relative path in the referencing model. This means that there is no change to make in our existing persistence schema and, therefore that there is backward-compatibility of your existing relative references.
- an intra-repository reference can sometimes be resolved at runtime as a remote URL. This means that such a reference can still be resolved by accessing the local file system but, in some circumstances (see table below), the relative path can also end up being mapped to a remote URL that is relative to the current provider, repository and branch.
The table below summarizes the various resolution strategies for intra-repository references. The necessary evolutions are highlighted in orange.
| Referencing modem | Reference | Resolution strategy in desktop app | Resolution strategy in browser app |
|---|---|---|---|
| not in a Git repo | relative path | read from file system | not resolved (refresh disabled) |
| absolute path | read from file system | not resolved (refresh disabled) | |
| internet link | GET internet link | GET internet link | |
| opened from local clone | relative path | read from file system | not resolved (refresh disabled) |
| absolute path | read from file system | not resolved (refresh disabled) | |
| internet link | GET internet link | GET internet link | |
| opened from Git provider | relative path | path mapped to URL for same provider, repository, and branch | path mapped to URL for same provider, repository, and branch |
| absolute path | not resolved (cannot map a local path that is absolute to a path in the remote repo) | not resolved (cannot map a local path that is absolute to a path in the remote repo) | |
| internet link | GET internet link | GET internet link |
In summary, when opening an intra-repository reference, the application:
- maps the URL of the referenced model to a path that is relative to the referencing model
- maps the relative path back to a URL for the same provider, repository and branch.
Cross-repository references
An cross-repository reference is an external or polyglot reference, from a model that belongs to a Git repository, to another model that belongs to another Git repository.
An cross-repository reference is different than an intra-repository reference in the sense that it is not meant to be relative to the provider, repository, or branch of the referencing model. An cross-repository reference points explicitly to a specific model in a specific branch of a specific repository hosted by a specific provider. It does not have to "follow" local clones, branches, and forks like an intra-repository reference. Conceptually, an cross-repository reference is nothing else than an internet link, accessible provided that the user has the appropriate authentication.
From a persistence perspective, cross-repository references are not stored as HTTP(S) URLs. Instead, the application rather store the metadata allowing to build the appropriate URL and apply the appropriate authentication when resolving the reference. For example
"link": "?g=github&o=hackolade&r=demo-models-read-only&f=merchandising%2FProduct+management-Oracle.hck.json&b=main"
User-experience
Given the added capabilities, the previous simple dialog has been changed to a new flow. The previous dialog:
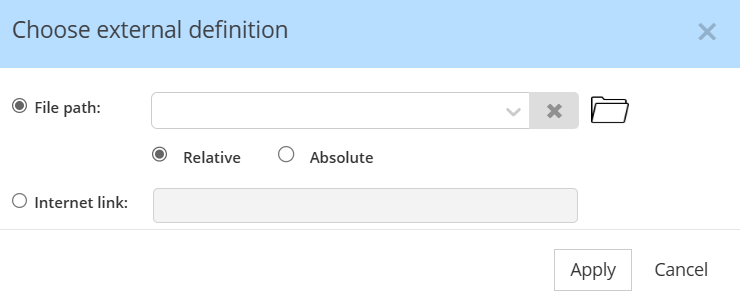
was opening the OS Open dialog.
The new dialog shows a simplified structure:
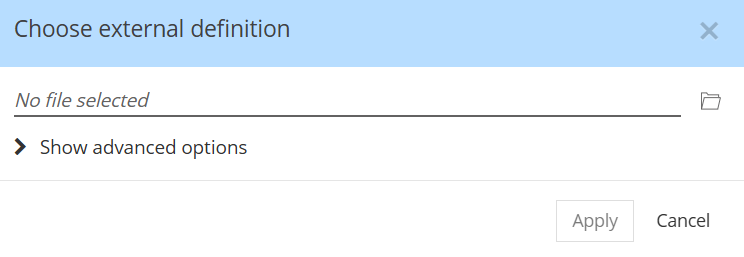
You are still able to reference an Internet link, or to use absolute paths, but these being edge cases, they are hidden for simplicity. To choose an absolute path, you must first choose the external file on your local file system.
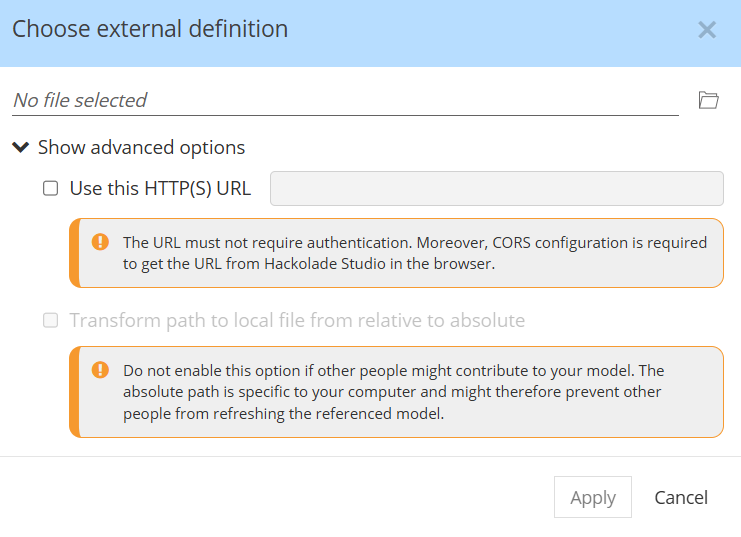
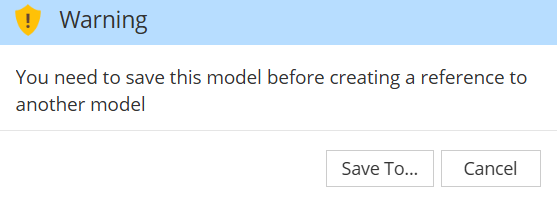
Note: in case your model is brand new and has never been saved before, you are first prompted to Save your model:
Open referenced data model from..
When you click the folder icon, a new screen allows to select either your local file system, or a repo from one of the configured providers:
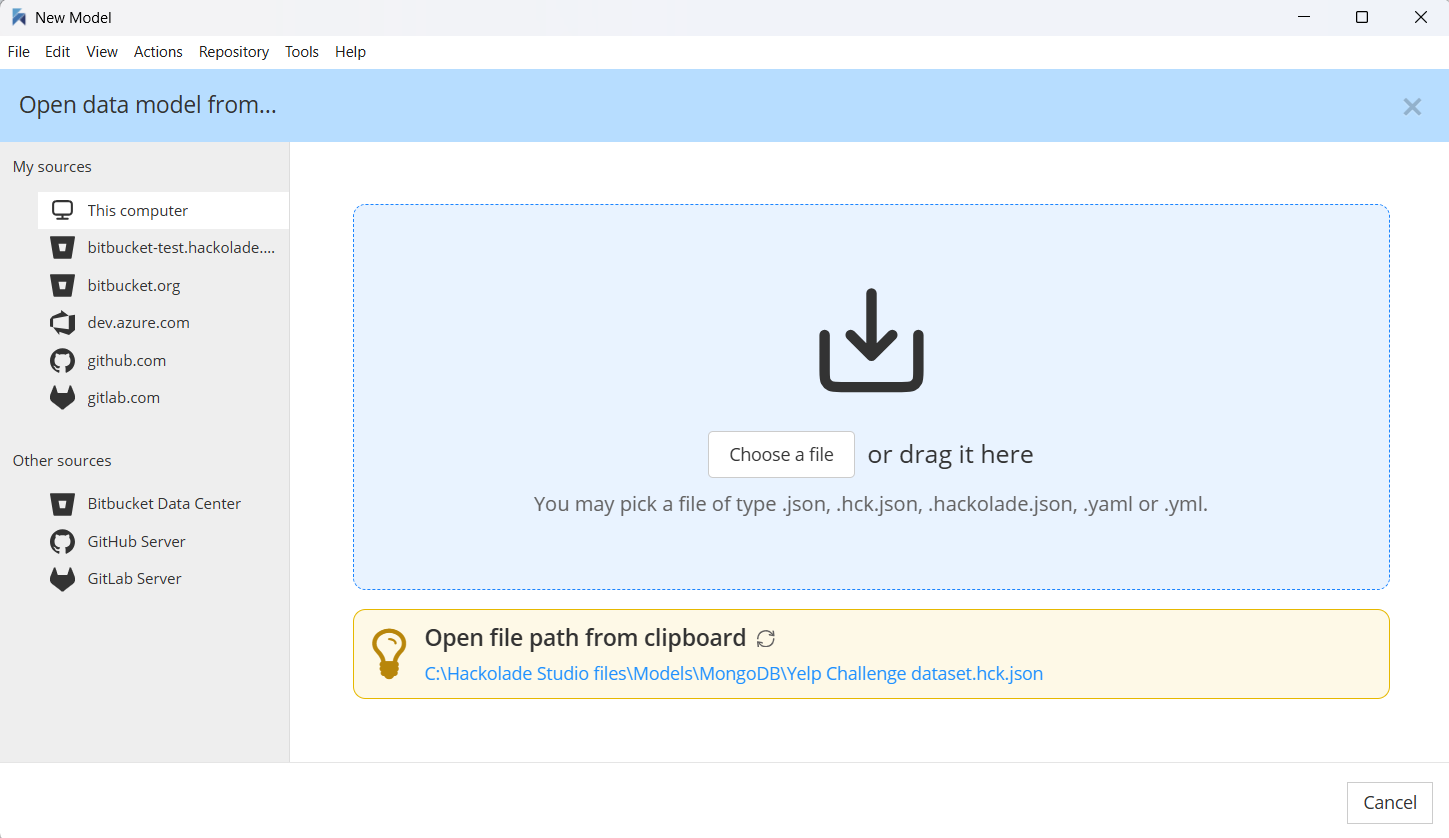
If in your clipboard you already a full file path (folder path plus file name), you can click on the link. If you want to select a file from your computer (in your locally-clone repo, or outside of it), you can click on the Choose file button, or drag the file name from OS explorer/finder.
If you want to reference a model in a Git repo, click first on the repo provider in the list on the left,
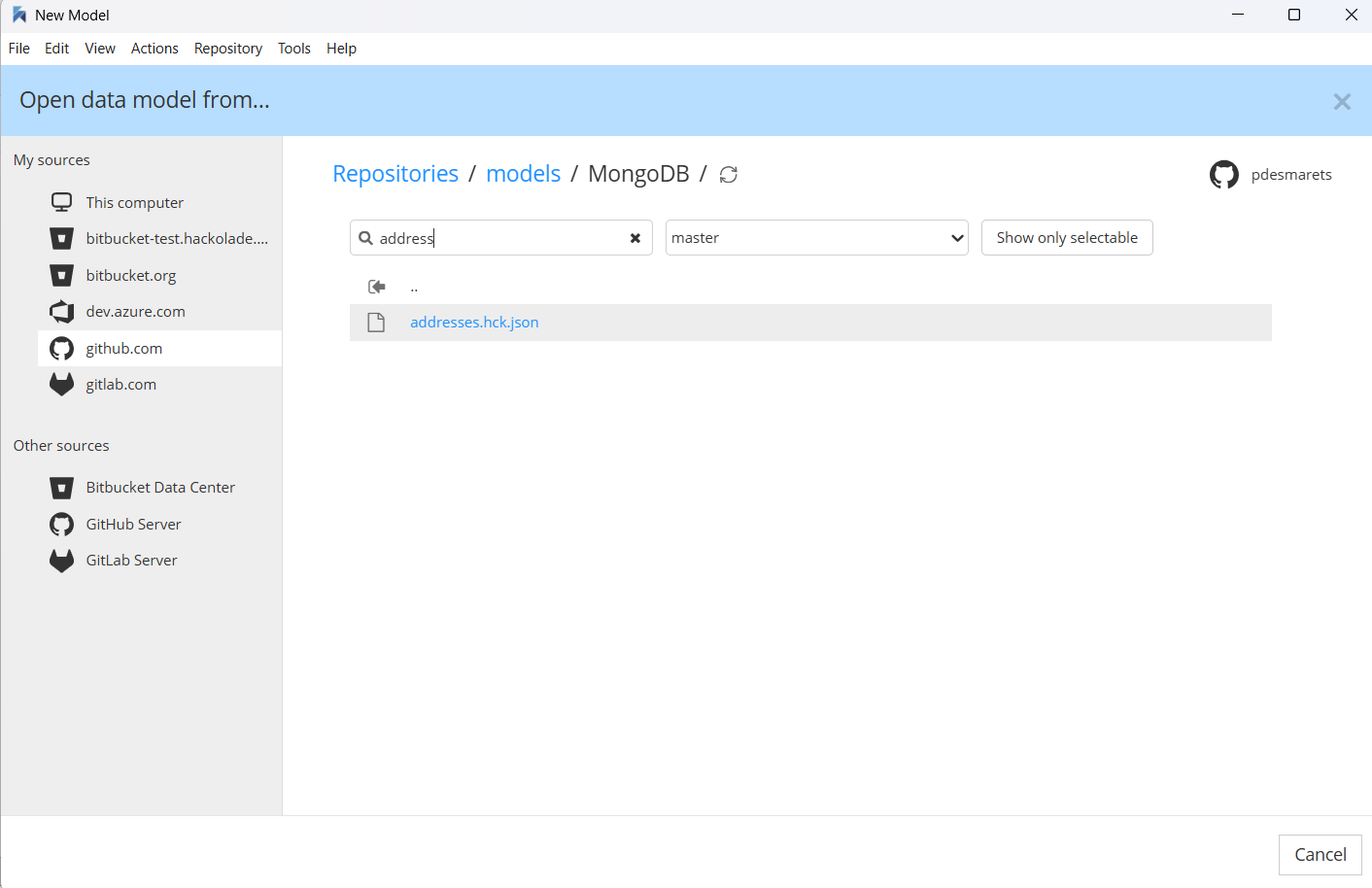
then select the file of your choice.