Db2
IBM Db2 is a family of relational databases for various platforms, developed by IBM. The brand name was originally styled as DB/2, then DB2 until 2017 and finally changed to its present form: Db2. Db2 is a relational database that delivers advanced data management and analytics capabilities for transactional workloads. This operational database is designed to deliver high performance, actionable insights, data availability and reliability, and it is supported across Linux, Unix and Windows operating systems.
While Db2 is also available for z/OS (mainframe), Hackolade currently has no intention to support connectivity to a mainframe, as we would have no test platform, except through the reverse-engineering of DDLs. We currently only support integration of Db2 for LUW.
Db2 on Cloud, formerly named "dashDB for Transactions", Db2 on Cloud is a fully managed, cloud SQL database with a high-availability option, offering independent scaling of storage and compute, and rolling security updates. Db2 on Cloud is deployable on both IBM Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
To perform data modeling for IBM Db2 with Hackolade, you must first download the Db2 plugin.
Hackolade Studio was specially adapted to support the data modeling of Db2, including schemas, tables and views, indexes and constraints, plus the generation of DDL Create Table syntax. Db2 initially supported the relational model, but was extended to support non-relational structures like JSON.
In particular, Hackolade Studio has the unique ability to model complex semi-structured JSON objects stored in text columns. We're not talking about functions that "flatten" JSON into standard columns, which runs the risk of inconsistencies, if not errors, when doing the Cartesian product of multiple complex data types. But about the storage of entire JSON documents. The reverse-engineering function, if it detects JSON documents, will sample records and infer the schema to supplement the DDL table definitions.
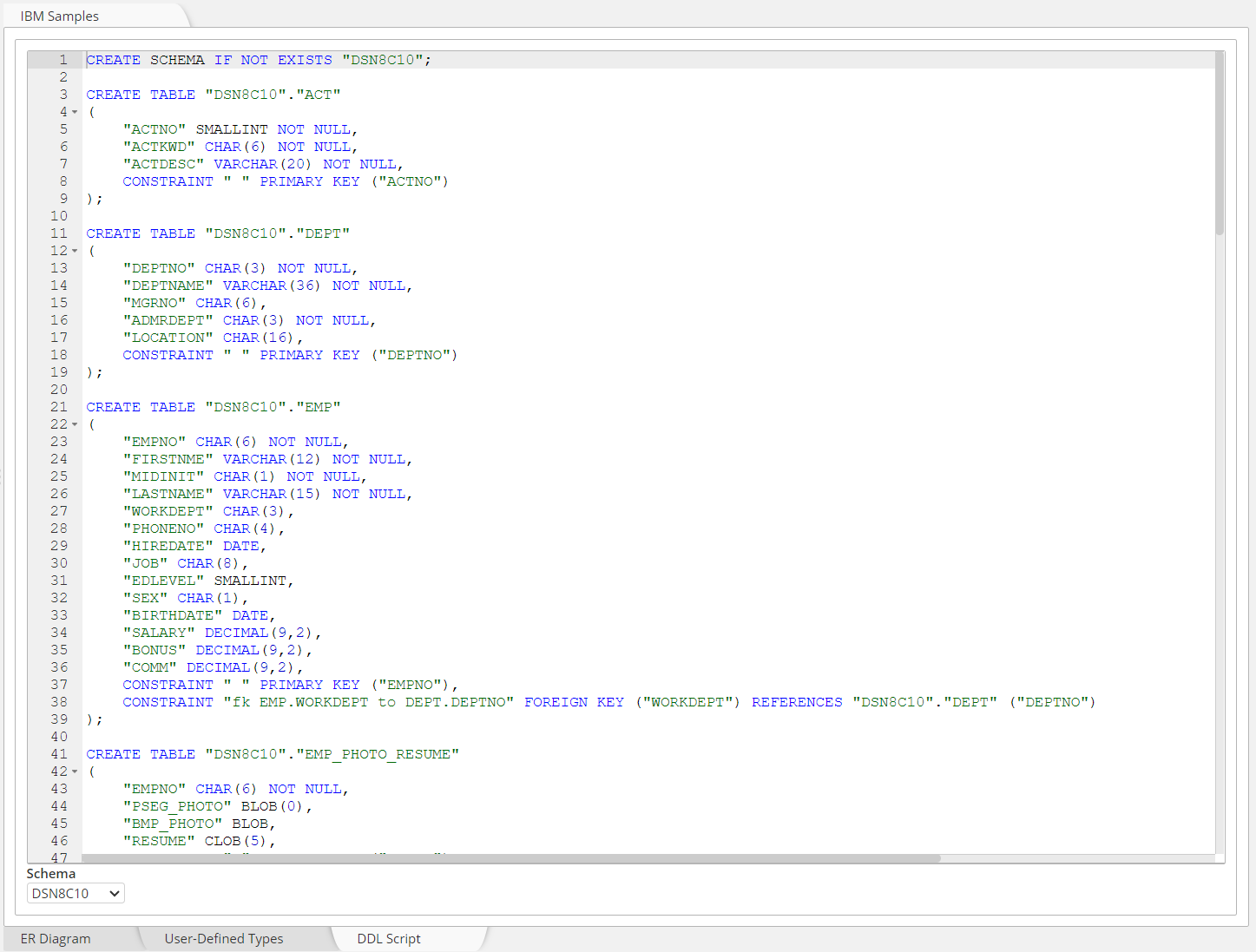
The data model in the picture below results from the data modeling of the IBM Samples database:

Schemas
The objects in a relational database are organized into sets called schemas. A schema is a collection of named objects that provides a logical classification of objects in the database. A schema provides a logical classification of objects in the database. The objects that a schema can contain include tables, indexes, table spaces, distinct types, functions, stored procedures, and triggers.
A single Hackolade model deals with a single database but can handle multiple schemas.
Tables
Tables are logical structures that Db2 maintains. Db2 supports several different types of tables. Tables are made up of columns and rows. The rows of a relational table have no fixed order. The order of the columns, however, is always the order in which you specified them when you defined the table.
At the intersection of every column and row is a specific data item, which is called a value.
A column definition has two basic components, the column name and the data type. A column contains values that have the same data type. Every table must have one or more columns, but the number of rows can be zero.
Unique, Primary, and Foreign Keys, plus Not Null, Check and Default constraints
A constraint is rules that Db2 enforces for column values to prevent duplicate values or set restrictions on data added to a table.
Db2 uses the following types of constraints.
The types of integrity constraint are described briefly below:
- A NOT NULL constraint prohibits a database value from being null.
- A unique constraint prohibits multiple rows from having the same value in the same column or combination of columns but allows some values to be null.
- A primary key constraint combines a NOT NULL constraint and a unique constraint in a single declaration. That is, it prohibits multiple rows from having the same value in the same column or combination of columns and prohibits values from being null.
- A foreign key constraint requires values in one table to match values in another table.
- A check constraint requires a value in the database to comply with a specified condition.
You can define constraints syntactically in two ways:
- As part of the definition of an individual column or attribute. This is called inline specification.
- As part of the table definition. This is called out-of-line specification.
Partitioning
Partitioned tables use a data organization scheme in which table data is divided across multiple storage objects, called data partitions or ranges, according to values in one or more table partitioning key columns of the table.
A data partition or range is part of a table, containing a subset of rows of a table, and stored separately from other sets of rows. Data from a given table is partitioned into multiple data partitions or ranges based on the specifications provided in the PARTITION BY clause of the CREATE TABLE statement.
Indexes
An index is an ordered set of pointers to rows of a table. Db2 can use indexes to improve performance and ensure uniqueness. Understanding the structure of Db2 indexes can help you achieve the best performance for your system.
Hackolade supports the most common types of Db2 indexes.
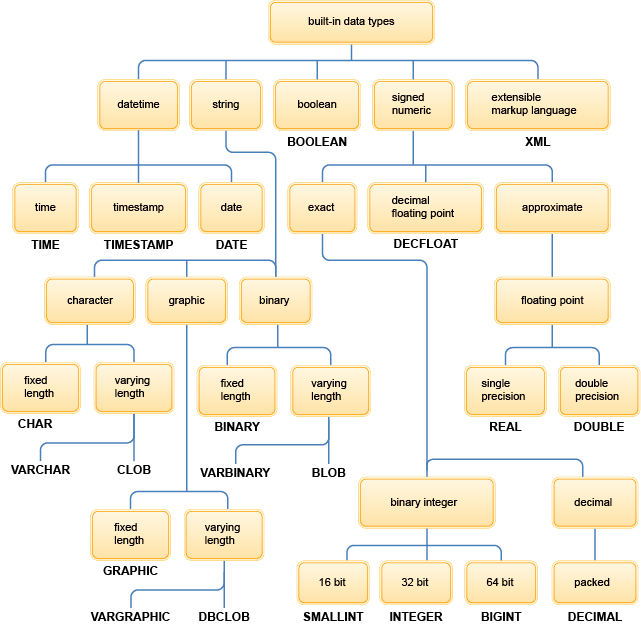
Data types
Every column in every Db2 table has a data type. The data type influences the range of values that the column can have and the set of operators and functions that apply to it. You specify the data type of each column at the time that you create the table. You can also change the data type of a table column. The new data type definition is applied to all data in the associated table when the table is reorganized.
Some data types have parameters that further define the operators and functions that apply to the column. Db2 supports both IBM®-supplied data types and user-defined data types. The data types that IBM supplies are sometimes called built-in data types.
Views
A view is an alternative way of representing data that exists in one or more tables. A view can include all or some of the columns from one or more base tables. A view is a named specification of a result table.
Triggers, Functions and Procedures
TBA
Forward-Engineering
Hackolade dynamically generates the DDL script to create schemas, tables, columns and their data types, indexes and constraints for the structure created with the application, as well as functions and procedures.
The script can also be exported to the file system via the menu Tools > Forward-Engineering, or via the Command-Line Interface.
If you store JSON documents in text, Hackolade allows for the schema design of those documents. However, the corresponding JSON structure is not forward-engineered in the DDL script, but is useful for developers, analysts and designers.
Reverse-Engineering
The Db2 instance can hosted on-premises, or on virtualized machines in a private or public cloud. Details on how to connect Hackolade to Db2 can be found on this page.
The Hackolade process for reverse-engineering of Db2 databases includes the execution of statements to discover schemas, tables, columns and their types, indexes and constraints. For JSON documents in text columns, Hackolade Studio performs statistical sampling of records followed by probabilistic inference of the JSON document schema.
For more information on IBM Db2 in general, please consult the website and documentation.